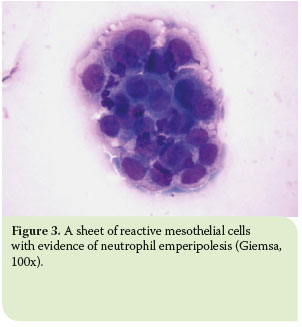
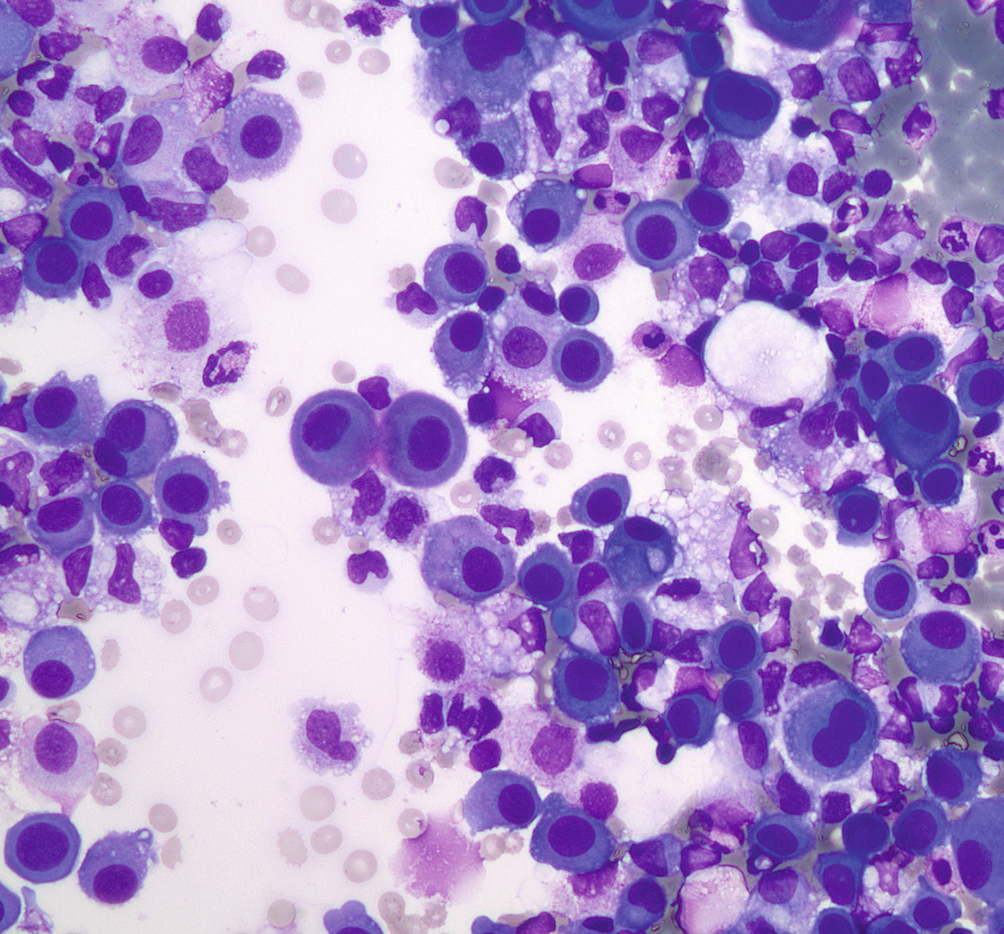
The suggestion that the presence of numerous often very reactive mesothelial cells in pleural aspirate makes the diagnosis of tuberculosis is unlikely confirmed mesothelial cells in pleural fluid.
Mesothelial cells in pleural fluid diagnosis.
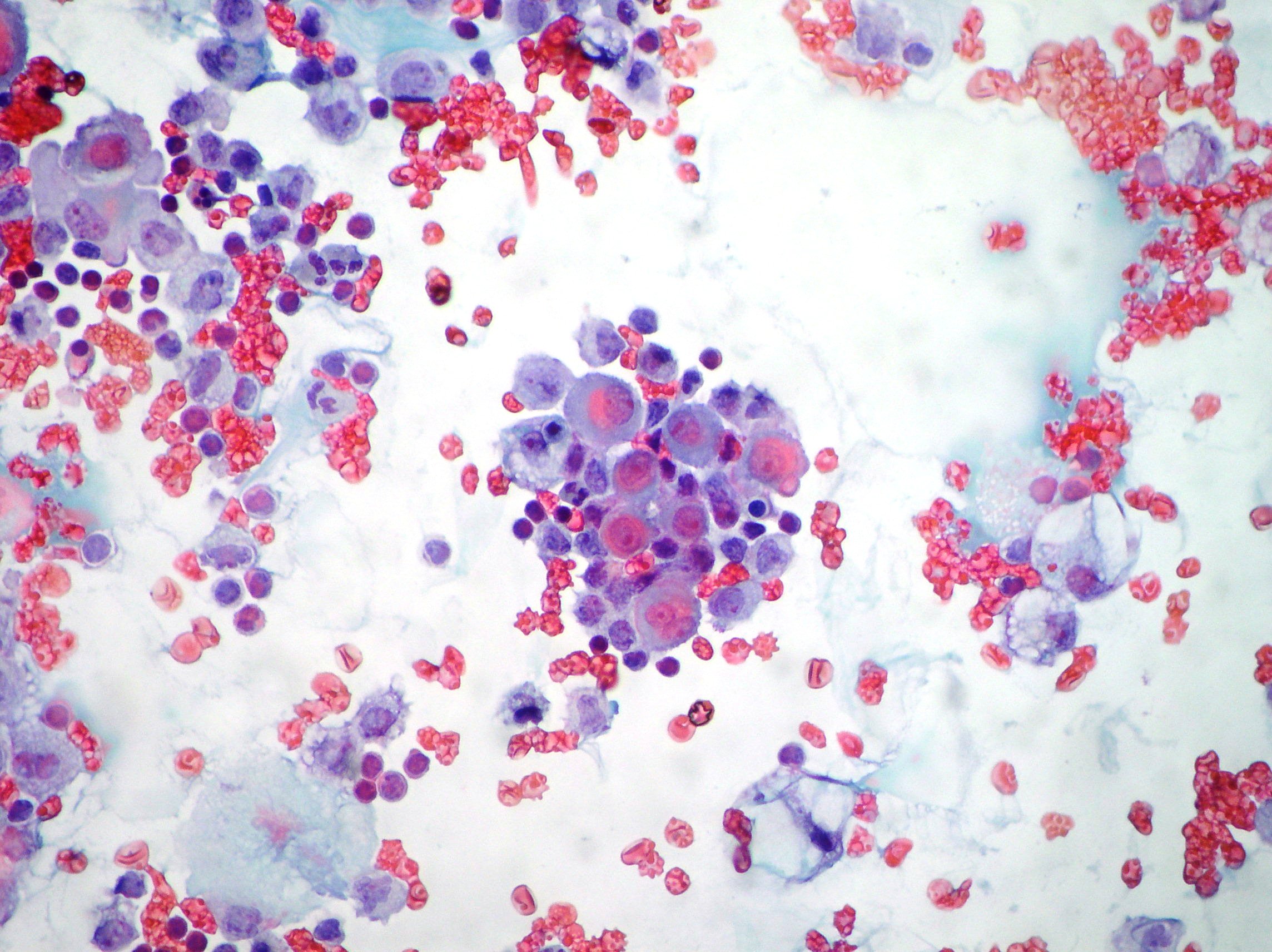
Actively dividing mesothelial cells can mimic an adenocarcinoma.
A patient may develop shortness of breath and vague chest pains while the fluid experiences a buildup in the chest cavity these are two of the most common.
Mesothelial cells in ascitic fluid mesothelial cells in ascitic fluid the associated tumor antigen 90k is known to possess properties similar.
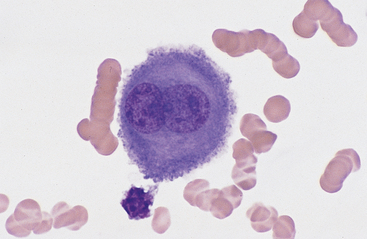
Hyperplastic mesothelial cells with slightly enlarged nuclei micronucleoli and a clear space or window between adjacent cells present singly and in small clusters.
Mesothelial cells in pleural fluid.
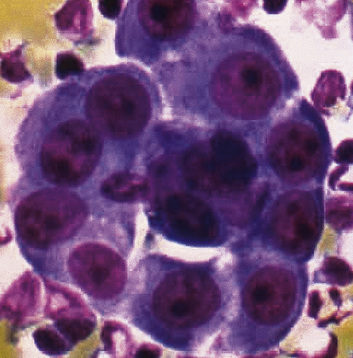
Larger clusters of hyperplastic mesothelial cells showing mildly nuclear atypia with small nucleoli.
Atypical mesothelial cell proliferation.
Reducing fluid volume provides the patient with symptom relief.
There are certain cells that line the pleura the thin double layered lining which covers the lungs chest wall and diaphragm which are known as mesothelial cells other than the pleura mesothelial cells also form a lining around the heart pericardium and the internal surface of the abdomen peritoneum.
This is known as pleural effusion.
The fluid can accumulate quickly if the mesothelial cells fail to function resulting in an unhealthy collection of fluids in the chest cavity.
The use of probrain natriuretic peptide in pleural fluid for the diagnosis of pleural effusions resulting from heart failure.